Hispanic Latino People in the US 2025
The Hispanic and Latino population in the United States has reached a historic milestone in 2025, representing one of the most significant demographic transformations in American history. With more than 68 million people identifying as Hispanic or Latino, this vibrant community now comprises approximately 20% of the total U.S. population, making them the nation’s largest and fastest-growing minority group. This remarkable growth trajectory reflects not only immigration patterns but also natural population increases, with Hispanic families contributing substantially to the nation’s demographic vitality through higher birth rates and a notably younger age structure compared to other population segments.
The presence and influence of Hispanic Latino Americans extend far beyond mere numbers, fundamentally reshaping the cultural, economic, social, and political landscape of the nation. From major metropolitan areas to small rural communities, Hispanic Latino communities have established themselves as essential contributors to American society, enriching the country with diverse traditions, languages, entrepreneurial spirit, and workforce participation. Understanding the current state of the Hispanic Latino population in 2025 is crucial for policymakers, educators, business leaders, and community organizations as they plan for an increasingly diverse American future where this demographic will play an even more central role in shaping the nation’s trajectory.
Interesting Stats & Facts About Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Fact Category | Statistic | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Total Population | 68 million people | Represents 20% of total U.S. population |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.8% annually | Accounts for 71% of total U.S. population growth between 2022-2023 |
| Median Age | 31.0 years | Nearly 8 years younger than national median of 38.9 years |
| Youth Population | 24.1% under age 18 | Higher than national average of 21.7% |
| Largest Origin Group | Mexican Americans | Comprise 59% of all Hispanic Americans |
| Congressional Representation | 56 members in 119th Congress | 6 senators and 50 House members |
| Languages Spoken | 68.2% speak Spanish at home | 28.7% speak English “less than very well” |
| Business Ownership | 465,202 employer businesses | Grew 44.4% between 2017-2022 |
| Life Expectancy | 81.3 years | Higher than national average of 78.4 years |
| College Enrollment | 18.4% of undergraduates | Over 3.6 million students in higher education |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey 2024, Bureau of Labor Statistics 2025, U.S. Congress Records 2025
The data presented in this table reveals the dynamic and youthful nature of the Hispanic Latino population in the United States. The 68 million Hispanic Americans represent a demographic force that contributed 71% of all U.S. population growth between 2022 and 2023, effectively serving as the primary engine of America’s demographic expansion. This growth is particularly remarkable when considering that the non-Hispanic population grew by only 0.2% during the same period, highlighting the vital role Hispanic communities play in preventing population decline across numerous states and metropolitan areas. The median age of 31 years positions the Hispanic population as significantly younger than the overall U.S. population, creating a demographic dividend that will sustain workforce growth and economic productivity for decades to come.
The concentration of 24.1% of the Hispanic population under age 18 translates to more than 16 million young people who will enter educational institutions, workforce markets, and civic participation over the next two decades. The dominance of Mexican Americans at 59% of the total Hispanic population reflects historical migration patterns and geographical proximity, while the growing representation in Congress with 56 members demonstrates increasing political influence and civic engagement. The 44.4% growth in Hispanic-owned employer businesses between 2017 and 2022 showcases the entrepreneurial spirit driving economic contributions, with these 465,202 businesses employing over 3.5 million workers and generating more than $653 billion in revenue. The life expectancy of 81.3 years, exceeding the national average, illustrates what researchers call the “Hispanic paradox”—better health outcomes despite facing socioeconomic challenges.
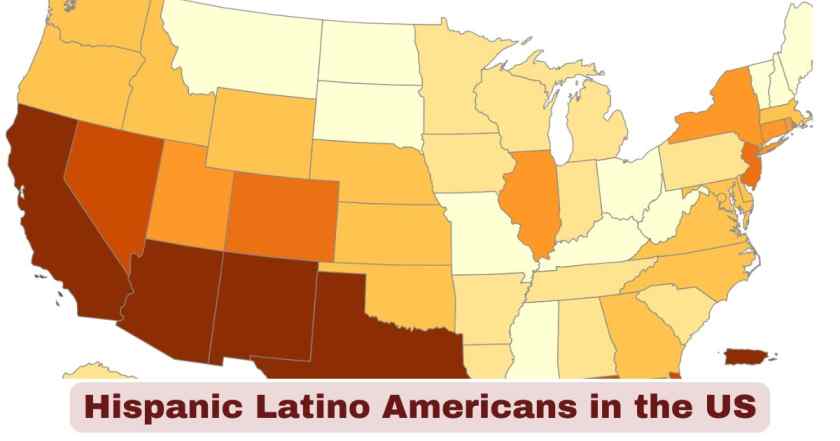
Hispanic Latino Population Distribution by State in US 2025
| State | Hispanic Population | Percentage of State Population | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 15.5 million | 39.4% | 1 |
| Texas | 12 million | 39.8% | 2 |
| Florida | 6 million | 26.5% | 3 |
| New York | 3.7 million | 19.0% | 4 |
| Arizona | 2.3 million | 31.6% | 5 |
| Illinois | 2.2 million | 17.4% | 6 |
| New Jersey | 2 million | 22.7% | 7 |
| Colorado | 1.3 million | 22.7% | 8 |
| New Mexico | 1 million | 48.6% | 9 |
| Georgia | 1.1 million | 10.3% | 10 |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau Vintage 2024 Population Estimates, American Community Survey 2024
The geographic distribution of Hispanic Latino Americans across U.S. states in 2025 demonstrates both traditional concentration patterns and expanding demographic reach throughout the nation. California maintains its position as the epicenter of Hispanic population with 15.5 million residents, though New Mexico leads in percentage terms at 48.6%, making it the only state where Hispanics constitute nearly half the total population. Texas follows closely with 12 million Hispanic residents at 39.8%, reflecting the state’s historical connections to Mexico and its continued role as a primary destination for Hispanic migration. The presence of 15 states with over 1 million Hispanic residents each illustrates that this demographic transformation extends far beyond traditional gateway states.
The data reveals that 27 states experienced Hispanic population growth that exceeded non-Hispanic growth between 2022 and 2023, with 13 states seeing their non-Hispanic populations decline while Hispanic populations increased, effectively preventing overall population loss. Florida’s 6 million Hispanic residents reflect significant Caribbean Hispanic communities, particularly Cuban, Puerto Rican, and Dominican populations concentrated in South Florida. The presence of substantial Hispanic communities in New York, Illinois, and New Jersey demonstrates continued urban concentration in major metropolitan areas. Meanwhile, states like Colorado, Nevada, and Arizona show how Hispanic population growth has transformed the demographics of the Mountain West region. This geographic distribution across 73% of U.S. metro areas experiencing population growth shows that the Hispanic demographic transformation affects suburban and rural communities nationwide, fundamentally reshaping American regional demographics.
Educational Attainment Among Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Education Level | Hispanic Latino Percentage | National Average | Growth Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| High School Graduation | 88.5% (ages 25-29) | 93.0% | Up from 58.2% in 1996 |
| Bachelor’s Degree or Higher | 22% (ages 25+) | 39% | Nearly doubled in past 2 decades |
| College Enrollment | 18.4% of undergraduates | N/A | 3.6 million students in 2025 |
| Graduate Students | 308,390 students | 10% of all graduate students | Growing representation |
| First-Generation College Students | 70% | 33% national average | Highest among ethnic groups |
| Hispanic-Serving Institutions | 67% attend HSIs | N/A | 465+ institutions nationwide |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau Current Population Survey 2025, National Center for Education Statistics 2025, National Student Clearinghouse Research Center 2025
Educational attainment among Hispanic Latino Americans has shown remarkable improvement over the past three decades, though significant gaps remain compared to other demographic groups. The high school graduation rate of 88.5% for Hispanic Americans ages 25-29 represents substantial progress from the 58.2% rate recorded in 1996, demonstrating a 30.3 percentage point increase that reflects enhanced educational access, family commitment to education, and targeted intervention programs. However, the 22% bachelor’s degree attainment rate for Hispanics ages 25 and older still lags behind the 39% national average, indicating persistent barriers to higher education completion. The enrollment of 3.6 million Hispanic students in postsecondary institutions makes them the largest minority group in higher education, with 18.4% of all undergraduate students identifying as Hispanic or Latino.
The concentration of 70% of Hispanic students as first-generation college attendees highlights both the educational mobility occurring within Hispanic families and the unique challenges these students face navigating higher education systems without parental guidance. The fact that 67% of Hispanic students attend Hispanic-Serving Institutions (HSIs)—colleges where at least 25% of undergraduate enrollment is Hispanic—demonstrates the critical role these specialized institutions play in providing culturally responsive education. Female Hispanic students comprise 58% of undergraduate enrollment, reflecting broader gender trends in higher education. The 308,390 Hispanic graduate students represent growing professional development and advanced degree pursuit, though they constitute only 10% of total graduate enrollment, suggesting continued underrepresentation at the highest educational levels that affects career advancement and earning potential.
Employment and Labor Force Participation of Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Employment Metric | Hispanic Latino Statistics | National Average | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Force Size | 31.8 million workers | 166.4 million total | 19% of U.S. workforce |
| Labor Force Participation Rate | 67.2% | 62.9% | 4.3 percentage points higher |
| Employment-Population Ratio | 63.8% | 60.3% | 3.5 percentage points higher |
| Unemployment Rate | 5.3% (August 2025) | 4.6% | Slightly elevated |
| Self-Employment Rate | 10.0% | 9.6% | Higher entrepreneurial activity |
| Median Weekly Earnings | $920 (Q2 2025) | $1,145 | $225 gap |
Data Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Current Population Survey 2025, Federal Reserve Economic Data 2025
The Hispanic Latino workforce has become an indispensable component of the American economy, with 31.8 million workers representing 19% of the total U.S. labor force in 2025, a proportion that has grown 69% since 2003 compared to just 6% growth among non-Hispanic workers. The labor force participation rate of 67.2% for Hispanics consistently exceeds the national average of 62.9%, driven primarily by the demographic composition of the Hispanic population, which has a larger concentration of people in prime working ages 25-54 years at 56% of the total. The employment-population ratio of 63.8% for Hispanics, which is 3.5 percentage points higher than the national average, demonstrates strong workforce attachment and economic contribution.
However, challenges persist in the form of higher unemployment rates at 5.3% compared to the 4.6% national average, reflecting educational attainment gaps, occupational segregation, and potential discrimination in hiring practices. The median weekly earnings of $920 for full-time Hispanic workers falls $225 below the national median, representing a significant wage gap that contributes to income inequality. The 10% self-employment rate among Hispanic workers, higher than the 9.6% for non-Hispanic workers, showcases entrepreneurial initiative, with foreign-born Hispanics showing particularly high self-employment at 14.1%. Hispanic workers are concentrated in construction, accommodation and food services, administrative support, and manufacturing sectors, with underrepresentation in higher-paying professional and managerial occupations. The Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts that the Hispanic labor force will account for 21.9% of the overall workforce by 2032, cementing their role as primary drivers of future labor market growth.
Income and Economic Status of Hispanic Latino Households in US 2025
| Economic Indicator | Hispanic Latino Data | National Comparison | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median Household Income | $70,950 (2024) | $83,730 | $12,780 gap |
| Median Earnings (Full-Time Workers) | $50,430 (2024) | $60,070 | $9,640 gap |
| Poverty Rate | 16.9% (2022) | 11.5% | 5.4 percentage points higher |
| Median Net Worth | $52,190 (2020) | $195,600 non-Hispanic | $143,410 wealth gap |
| Homeownership Rate | 49.9% (2023) | 66.0% | Lower but growing |
| Uninsured Rate | 17.0% (2024) | 8.2% | 8.8 percentage points higher |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau Current Population Survey 2025, Federal Reserve Survey of Consumer Finances 2021, American Community Survey 2024
The economic status of Hispanic Latino households has shown notable improvements in recent years, though substantial disparities persist compared to the overall U.S. population. The median household income of $70,950 for Hispanic families in 2024 represents a 5.5% increase from 2023 and a 4.3% increase from pre-pandemic levels in 2019, making Hispanics the only racial or ethnic group to experience significant income growth compared to 2019 levels. However, the $12,780 gap below the national median household income of $83,730 reflects ongoing challenges related to educational attainment, occupational distribution, and wage discrimination. The median earnings of $50,430 for full-time, year-round Hispanic workers increased 4.9% from 2023, but remains substantially below the national figure.
The poverty rate of 16.9% for Hispanic Americans in 2022 is nearly 50% higher than the overall U.S. poverty rate of 11.5%, affecting approximately 10.7 million Hispanic individuals. The median net worth of $52,190 for Hispanic households represents approximately 27% of the $195,600 median for non-Hispanic white households, illustrating profound wealth inequality that limits intergenerational mobility and asset accumulation. However, positive trends include the homeownership rate of 49.9%, with home equity accounting for 33% of Hispanic household wealth in 2022, up from 26.7% in 2013. The dramatic uninsured rate of 17.0% among Hispanics—more than double the national rate—creates significant barriers to healthcare access and contributes to health disparities. Despite these challenges, Hispanic consumer purchasing power reached $2.8 trillion in 2025, making this demographic the most sought-after consumer market by corporations across all sectors.
Hispanic Latino Business Ownership and Entrepreneurship in US 2025
| Business Metric | Hispanic Latino Statistics | Growth Rate | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employer Businesses | 465,202 firms (2022) | 44.4% growth (2017-2022) | 7.9% of all U.S. employer businesses |
| Total Businesses Owned | 5 million+ firms | 14.5% of all business owners | Includes non-employer businesses |
| Employees | 3.55 million workers | 14.1% increase (2021-2022) | Growing job creation |
| Annual Revenue | $653 billion | 18.9% increase (2021-2022) | Substantial economic contribution |
| Business Formation Rate | 82% of new businesses | 3 times national average | Highest among ethnic groups |
| Self-Employment | 10.0% of workers | Higher than 9.6% national | Strong entrepreneurial culture |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau Annual Business Survey 2022, Small Business Administration 2024, Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative 2024
Hispanic Latino entrepreneurship represents one of the most dynamic forces in the American economy, with business ownership growth far outpacing other demographic groups. The 465,202 Hispanic-owned employer businesses recorded in 2022 reflect a remarkable 44.4% increase since 2017, compared to just 0.46% annual growth for all U.S. employer businesses during the same period. This extraordinary 7.7% average annual growth rate demonstrates the entrepreneurial vitality of the Hispanic community, with Latinos starting 82% of all new businesses in the United States at a rate three times the national average. Including both employer and non-employer firms, Hispanic Americans now own over 5 million businesses, representing 14.5% of all business owners nationwide.
These Hispanic-owned businesses employed 3.55 million workers in 2022 and generated $653 billion in total revenue, making substantial contributions to local economies and tax bases across the nation. The 18.9% revenue increase between 2021 and 2022 indicates not only business proliferation but also the growing scale and success of existing enterprises. Hispanic-owned businesses grew in 204 of 227 metro areas (89.9%) between 2017 and 2022, demonstrating widespread geographic expansion beyond traditional Hispanic population centers. Despite this impressive growth, Hispanic-owned businesses remain underrepresented at 7.9% of all employer businesses compared to the 19.1% Hispanic population share, suggesting substantial potential for future business formation and economic development. Key industries for Hispanic entrepreneurs include construction, professional services, retail trade, food services, and increasingly, technology and information services.
Health and Wellbeing of Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Health Indicator | Hispanic Latino Data | National Comparison | Disparity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Life Expectancy | 81.3 years | 78.4 years | 2.9 years longer |
| Uninsured Rate | 17.0% | 8.2% | 2.1 times higher |
| No Primary Care Provider | 32% | 24% | 8 percentage points higher |
| Diabetes Prevalence | Higher rates | National average | Leading health concern |
| Healthcare Visit (Past 12 Months) | 70% | 82% | 12 percentage points lower |
| Language Barrier | 28.7% speak English “less than very well” | N/A | Access challenge |
Data Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2025, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 2025, American Community Survey 2024
The health profile of Hispanic Latino Americans presents a complex picture characterized by the “Hispanic paradox”—the phenomenon where Hispanics demonstrate better overall health outcomes and longer life expectancy at 81.3 years despite facing socioeconomic disadvantages and limited healthcare access. This 2.9-year advantage over the national average of 78.4 years has been attributed to dietary patterns, strong family support systems, and potential healthy migrant effects. However, this aggregate advantage masks significant health challenges and disparities affecting the Hispanic community. The dramatically elevated uninsured rate of 17.0%—more than double the 8.2% national rate—creates substantial barriers to preventive care, routine checkups, and chronic disease management.
Only 70% of Hispanic adults report seeing a healthcare provider in the past 12 months, compared to 82% nationally, and 32% lack a regular primary care provider versus 24% of all Americans. Language barriers compound healthcare access challenges, with 28.7% of the Hispanic population speaking English “less than very well,” making patient-provider communication difficult and limiting understanding of treatment options. Diabetes emerges as the leading health concern for Hispanic families, with 19% of survey respondents identifying it as their biggest health issue—the highest percentage among all ethnic groups. Hispanic Americans also face elevated rates of obesity, certain cancers (cervical, liver, stomach), and chronic liver disease. The combination of high uninsured rates, language barriers, cultural factors, and limited access to culturally competent care creates systemic health inequities that demand policy attention and community-based health initiatives.
Political Participation and Representation of Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Political Metric | Hispanic Latino Data | Representation Level | Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congressional Members | 56 members (119th Congress) | 6 senators, 50 House members | Up from 14 members 40 years ago |
| Latina State Legislators | 214 members | 2.9% of state legislators | Record high in 2025 |
| Latina Governors | 1 active (Michelle Lujan Grisham) | Only 2 ever elected | Both from New Mexico |
| Voter Participation | 10% of 2024 voters | Growing electorate | Critical swing state influence |
| Democratic Identification | 50% | Compared to 40% Republican | 10% independent |
| Gender Gap | Women 60% favorable to Democrats | Men 45% favorable | Significant divide |
Data Source: U.S. Congress Records 2025, Center for American Women and Politics 2025, AP VoteCast 2024
The political representation and participation of Hispanic Latino Americans has expanded significantly, though still lags behind their population share. The 56 Hispanic or Latino members serving in the 119th Congress—including 6 senators and 50 House representatives—represents a dramatic increase from just 14 members in the 99th Congress four decades ago, all of whom were male. This growth reflects both increased Hispanic population size and enhanced civic engagement, though Hispanic representation at 10.4% of Congress remains below the 20% population share. Among House members, 38 identify as Democrats and 12 as Republicans, with 19 women serving, illustrating both partisan distribution and growing female representation.
At the state level, 2025 marked a record high for Latina representation in state legislatures with 214 members holding seats, comprising 2.9% of all state legislators. Of these, 182 are Democrats, 31 Republicans, and 1 nonpartisan, showing strong Democratic affiliation. New Mexico Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham stands as the only active Latina governor in 2025, one of only two Latinas ever elected governor in U.S. history. In the 2024 presidential election, Hispanic voters constituted approximately 10% of the electorate, with their support in swing states like Arizona playing a crucial role. About half of Hispanic voters identified as Democrats, 40% as Republicans, and 10% as independents, showing more political diversity than often assumed. A notable gender divide emerged, with 60% of Hispanic women holding favorable views of Democratic candidates compared to only 45% of Hispanic men, suggesting increasingly complex political dynamics within the Hispanic electorate that both parties must navigate.
Hispanic Latino Age Distribution and Generational Demographics in US 2025
| Age Group | Hispanic Population | Percentage of Total Hispanic | National Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 18 Years | 16.4 million | 24.1% | 21.7% nationally |
| 18-24 Years (Gen Z) | 5.8 million | 8.5% | Peak college/workforce entry |
| 25-44 Years (Millennials) | 21.2 million | 31.2% | Prime working age |
| 45-64 Years (Gen X) | 16.5 million | 24.3% | Peak earning years |
| 65+ Years (Boomers+) | 8.1 million | 11.9% | 17.3% nationally |
| Median Age | 31.0 years | Youngest major group | 38.9 years national median |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey 2024, Population Estimates 2024
The age distribution of Hispanic Latino Americans in 2025 reveals a remarkably youthful demographic profile that distinguishes this population from all other major racial and ethnic groups in the United States. With a median age of just 31.0 years—nearly 8 years younger than the overall U.S. median age of 38.9 years—the Hispanic population possesses a demographic vitality that will drive American demographic growth for decades. The concentration of 24.1% under age 18 represents 16.4 million young people who will shape America’s educational institutions, cultural landscape, and future workforce. This youth bulge stands in stark contrast to the aging non-Hispanic white population, which has a median age exceeding 44 years and where only 18.7% are under 18 years old.
The 31.2% of Hispanics in the prime working ages of 25-44 years translates to 21.2 million people entering peak productivity, family formation, and homebuying years, creating enormous consumer demand and economic activity. The relatively small proportion of 11.9% aged 65 and older—compared to 17.3% nationally—means the Hispanic population currently places lower demands on Social Security, Medicare, and elder care systems while contributing disproportionately to payroll taxes and workforce growth. However, this will shift dramatically as the population ages, with projections indicating the Hispanic population aged 65+ will grow from 8.1 million in 2025 to approximately 19.9 million by 2060, making them the largest minority elderly population. The generational composition shows 40% of Hispanics belong to Gen Z or younger, the highest percentage of any ethnic group, positioning Hispanic youth as a decisive force in shaping American culture, politics, consumer trends, and technological adoption.
Hispanic Latino Household and Family Structure in US 2025
| Family Structure Metric | Hispanic Statistics | National Average | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Hispanic Families | 14.65 million households | N/A | 13.7% of all U.S. families |
| Average Household Size | 3.66 people | 3.15 people | 0.51 people larger |
| Family Households with Children | 4.28 people average | 3.8 people | Significantly larger |
| Married Two-Parent Families | 55% of children | 67% nationally | Cultural variations |
| Single-Parent Households | 30% of children | 25% nationally | Economic challenges |
| Multigenerational Households | 32.1% | 17.7% | Nearly double national rate |
| Cohabiting Partner Families | 12% of children | 8% nationally | Alternative family formation |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey 2024, Current Population Survey 2025, Hispanic Research Center 2025
The family structure of Hispanic Latino households in 2025 demonstrates distinctive patterns that reflect cultural values, economic circumstances, and intergenerational support systems. Hispanic families average 3.66 people per household, substantially larger than the 3.15 national average, with families containing children averaging 4.28 people. This larger household size reflects both higher fertility rates—with Hispanic women ages 15-50 experiencing 76 births per 1,000 women compared to 53 per 1,000 for non-Hispanic whites—and greater likelihood of extended family co-residence. The 14.65 million Hispanic families represent 13.7% of all American families, and these households are more likely than the general population to include multiple generations, with 32.1% of Hispanic households classified as multigenerational compared to just 17.7% of non-Hispanic households.
Among Hispanic children, 55% live with two married parents, 12% with cohabiting parents, 30% in single-parent households, and 3% with no parent present in the household. These family structures vary significantly by national origin and generation, with Cuban Americans and South Americans showing higher rates of two-parent families, while Puerto Ricans have higher single-parent household rates at 26.1%. Notably, Hispanic children in low-income households with immigrant parents are twice as likely to live with two married parents (58%) compared to those with only U.S.-born parents (29%), reflecting stronger traditional family structures among recent immigrants. The prevalence of multigenerational living arrangements serves economic purposes, with families pooling resources to afford housing, childcare, and eldercare, but also reflects cultural values emphasizing family unity and interdependence. Mexican American families average 4.06 people, the largest among Hispanic subgroups, compared to 3.39 for Puerto Ricans and 3.31 for Cubans, demonstrating internal diversity within the broader Hispanic population.
Housing and Homeownership Among Hispanic Latino Americans in US 2025
| Housing Metric | Hispanic Latino Data | National Benchmark | Progress Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homeownership Rate | 49.9% (Q2 2025) | 66.0% | 16.1 percentage point gap |
| Total Hispanic Homeowners | 9.8 million households | N/A | Record high in 2025 |
| New Hispanic Homeowners (2024) | 238,000 households | 35% of national growth | Largest of any group |
| Multigenerational Homeownership | 6.3 million households | N/A | 32.1% of Hispanic households |
| FHA Loan Utilization | 2x national rate | Baseline | Higher reliance on government programs |
| Projected Growth by 2040 | 70% of new homeowners | N/A | Will dominate market growth |
Data Source: U.S. Census Bureau Housing Vacancy Survey Q2 2025, National Association of Hispanic Real Estate Professionals 2024, Federal Reserve FRED Database 2025
Hispanic Latino homeownership reached a historic milestone in 2025 with 9.8 million Hispanic households owning their homes, representing the highest absolute number ever recorded despite a slight decrease in the overall homeownership rate to 49.9%. In 2024 alone, the Hispanic community added 238,000 new homeowner households, accounting for 35% of the nation’s total net increase in homeownership and surpassing all other racial and ethnic groups for the second consecutive year. This growth occurred even as rising home prices and elevated interest rates challenged affordability nationwide, with the median home price reaching $439,894 in 2025. The homeownership rate of 49.9%, though down 0.5 percentage points from 2023, remains on an upward trajectory over the past decade, growing from approximately 45.6% in 2016, representing nearly 1 percentage point increase every two years.
The 16.1 percentage point gap between Hispanic homeownership at 49.9% and the 66% national rate reflects systemic barriers including lower median incomes, accumulated wealth disparities, credit access challenges, and historical discrimination through redlining and lending practices. However, Hispanic families demonstrate remarkable determination and resourcefulness in achieving homeownership through multigenerational strategies, with 6.3 million or 32.1% of Hispanic households classified as multigenerational compared to 17.7% of non-Hispanic households, allowing families to pool financial resources. Hispanic borrowers utilize FHA loans at twice the rate of non-Hispanic borrowers, taking advantage of lower down payment requirements (3.5%) and more flexible credit standards. Family members frequently cosign loans to help each other qualify, with brothers cosigning for siblings being a common practice. By 2040, projections indicate Hispanic Americans will account for 70% of all net new homeowners** in the United States, effectively dominating housing market growth as younger Hispanic millennials and Gen Z members enter prime homebuying years. The most affordable markets for Hispanic homebuyers include St. Louis, Pittsburgh, Columbia (South Carolina), Wichita, and Amarillo, while California markets remain among the least affordable despite having the nation’s largest Hispanic population.
Hispanic Latino Military Service and Veterans in US 2025
| Military Metric | Hispanic Latino Statistics | Representation | Trend Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Hispanic Veterans | 1.5 million | 8% of veteran population | Up 25% since 2008 |
| Active Duty Hispanic Service | 17-18% of forces | 305,000+ members | Growing representation |
| Marine Corps Hispanic Share | 23-26% | Highest of all branches | Strong presence |
| Gulf War Era II Veterans | 665,000 | 45% of Hispanic veterans | Post-9/11 generation |
| Officer Representation | 8% | 5% general/flag officers | Severe underrepresentation |
| Projected Growth by 2045 | 1.55 million veterans | 13% of veteran population | 36% of minority veterans |
Data Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Veterans Statistics 2023-2024, U.S. Department of Defense Personnel Statistics 2025, Department of Veterans Affairs 2025
Hispanic Latino military service has been a hallmark of American patriotism for generations, with 1.5 million Hispanic veterans comprising 8% of the total U.S. veteran population in 2023-2024, representing a 25% increase from 1.2 million in 2008. This growth occurred during a period when the overall veteran population declined by 20%, demonstrating the expanding role of Hispanics in America’s armed forces. Currently, Hispanic Americans make up approximately 17-18% of active-duty military personnel, with over 305,000 service members, making them slightly underrepresented relative to their 19-20% share of the overall population but overrepresented among those eligible to serve. The U.S. Marine Corps leads all branches with 23-26% Hispanic representation, followed by the Army and Navy at 18%, and the Air Force at 17%.
Among Hispanic veterans, 45% or 665,000 individuals served during Gulf War Era II (September 2001 to present), making this the largest cohort, while 21% or 309,000 served during Gulf War Era I (August 1990 to August 2001), and 18% or 269,000 served during World War II, Korean War, and Vietnam-era. Despite comprising 17-18% of enlisted personnel, Hispanic service members represent only 8% of the officer corps and a mere 1% of general and flag officers, revealing severe underrepresentation in senior military leadership that advocates characterize as failing to “mirror the face of America.” Over 60 Hispanic Americans have received the Medal of Honor, the nation’s highest military decoration, including historic figures like Pvt. Marcelino Serna in World War I and Medal of Honor recipient Master Sergeant Roy Benavidez. By 2045, projections indicate Hispanic veterans will reach 1.55 million, comprising 13% of the total veteran population and 36% of all minority veterans, cementing their role as the largest minority veteran group and requiring enhanced focus on culturally competent VA services, mental health support, and leadership development programs.
The trajectory of the Hispanic Latino population in the United States through 2025 and beyond presents a compelling narrative of continued demographic, economic, and social transformation that will fundamentally shape America’s future. Census Bureau projections indicate that the Hispanic population will reach approximately 111 million people by 2060, constituting 28% of the total U.S. population and effectively doubling current numbers. This growth, driven primarily by natural increase rather than immigration, ensures sustained demographic vitality even as immigration patterns fluctuate. The exceptionally young age structure of the Hispanic population, with a median age of 31 years, positions this community as the primary source of workforce replenishment as Baby Boomers retire, with Hispanic workers expected to account for nearly 22% of the labor force by 2032. Educational attainment continues improving, with college enrollment and degree completion rates rising faster for Hispanics than for other groups, suggesting enhanced earning potential and occupational mobility for future generations.
The economic influence of Hispanic Americans will expand dramatically, with purchasing power projected to exceed $3 trillion and entrepreneurial activity continuing to outpace national averages, creating jobs and driving innovation across industries. However, realizing this potential requires addressing persistent challenges including educational achievement gaps, wage disparities, wealth inequality, healthcare access barriers, and systemic discrimination. Policymakers must prioritize bilingual education, affordable higher education, healthcare coverage expansion, small business support, and civil rights enforcement to ensure equitable opportunities. The increasing political sophistication and engagement of the Hispanic electorate, particularly among younger, U.S.-born generations, will reshape American politics as both major parties compete for support. The success of Hispanic Latino Americans in overcoming barriers and maximizing their contributions will not only determine outcomes for this community but will significantly influence America’s overall prosperity, social cohesion, and global competitiveness in the decades ahead.
Disclaimer: This research report is compiled from publicly available sources. While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, no representation or warranty, express or implied, is given as to the completeness or reliability of the information. We accept no liability for any errors, omissions, losses, or damages of any kind arising from the use of this report.